UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) is a modern replacement for the traditional BIOS. It offers enhanced features like faster boot times, improved security, support for larger storage drives, and a graphical interface. On the other hand, Legacy BIOS uses 16-bit code with limited options and is considered outdated. Both UEFI and BIOS are types of firmware used during the startup process to initialize hardware and load the operating system. They also manage device boot order and allow users to customize settings. However, UEFI is more advanced, providing greater flexibility and features. This article explores the differences between UEFI and BIOS and how they function. Thunderbolt BIOS Assist Mode is a feature that integrates Thunderbolt technology with the computer’s firmware. In this mode, the BIOS pre-allocates PCIe and memory resources for the OS to manage Thunderbolt devices. This ensures that connecting or disconnecting Thunderbolt devices doesn't affect system performance or user experience. When enabled, Thunderbolt BIOS Assist Mode reserves specific resources for Thunderbolt devices, preventing disruptions in system operations. By allocating these resources in advance, it helps maintain stability and performance when using Thunderbolt peripherals. This mode aims to provide a seamless experience when working with Thunderbolt devices, avoiding issues like crashes or slowdowns due to hot-plugging. BIOS initializes and tests hardware components before loading the operating system. Its main functions include Power-on Self-Test (POST), configuration of hardware settings, boot order management, and system settings. Here are some key features of BIOS mode: Yes, in some cases, you may need to enable Thunderbolt in the BIOS before using Thunderbolt 3 hardware. Certain systems require manual activation in the BIOS. The steps vary depending on the manufacturer and BIOS version. Consult your manual or the manufacturer for guidance. A BIOS update might be necessary to activate Thunderbolt capabilities. Always seek professional advice if unsure about updating the BIOS. UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) is a modern standard that replaces the traditional BIOS. It provides faster boot times, better security, support for larger disks, and a graphical interface. UEFI boot mode refers to the method by which the system firmware loads the operating system during startup. Unlike traditional BIOS, UEFI stores initialization information in .efi files on the EFI System Partition (ESP). This allows direct booting of the OS without going through the BIOS self-test, resulting in faster startup times. UEFI supports larger storage drives, secure boot via Secure Boot, and graphical interfaces during boot. While many refer to UEFI as "BIOS," most modern systems use UEFI firmware instead. Choosing between UEFI and Legacy BIOS depends on your system's requirements and preferences. Here are the main differences: Changing Thunderbolt settings in the BIOS is a straightforward process. Here's a general guide: To unlock advanced settings in the BIOS, follow these steps: If the above steps don't work, try alternative methods such as pressing CTRL+F10 and CTRL+F11 during startup, or using Fn+Tab three times. If none of these work, your system may not support unlocking advanced settings. While BIOS and UEFI serve similar purposes, their underlying mechanisms differ significantly. UEFI is the preferred choice for modern systems, offering better performance and security. However, upgrading a legacy motherboard to UEFI is not possible, so a hardware upgrade would be required. Are you using a new system with UEFI or an older one with BIOS? The main difference between UEFI and BIOS lies in their architecture and capabilities. While BIOS uses 16-bit mode and has a limited user interface, UEFI uses 32-bit or 64-bit mode and offers a more advanced graphical user interface. UEFI is a 32-bit or 64-bit program written in C, while Legacy BIOS is a 16-bit assembly language program that runs only in real mode. UEFI provides more addressable memory and advanced features compared to BIOS. Modifying BIOS settings can be risky, so always exercise caution. Incorrect changes can prevent the computer from starting or damage the motherboard. Ensure compatibility, back up your data, and follow manufacturer guidelines before making any changes. To check your firmware type, go to the System Details page, click the Drive Encryption tab, and look for the firmware type. It will show either BIOS or EFI (UEFI). Legacy BIOS mode is compatible with older hardware and operating systems that may not support UEFI. If you're using older hardware or software, BIOS might be necessary. It is often simpler and more straightforward for basic tasks. UEFI is a specification that connects a computer's firmware to its operating system. Although it is expected to replace BIOS, it is backward compatible with it. Hence, people sometimes refer to UEFI as BIOS. UEFI mode is faster than legacy BIOS, offering quicker boot times, enhanced security, and support for larger storage devices. It is the preferred choice for modern systems. Water Treatment Skid,Commercial Ultrafiltration Skid,Commercial Ro Water Purifier,Skid-Mounted Water Treatment Systems Foshan Hongjun Water Treatment Equipment Co. Ltd , https://www.hjwastewatertreatment.com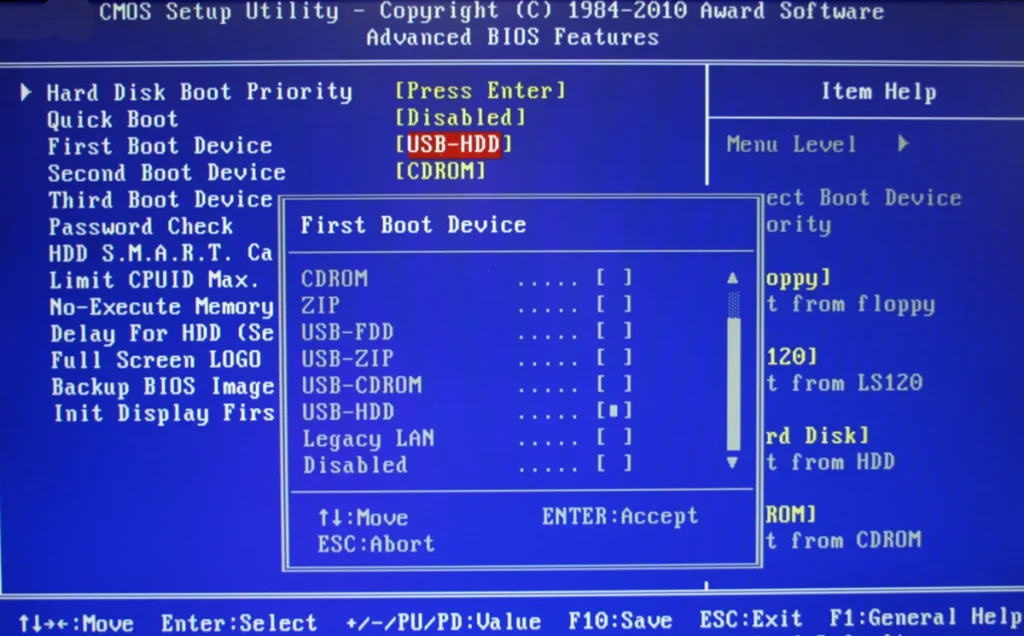
What is Thunderbolt BIOS Assist Mode?
What Does BIOS Mode Do?
Do I Need To Enable Thunderbolt In The Bios?
What is UEFI Boot Mode?
Functions of UEFI Boot Mode:
What Is The Difference Between UEFI And Legacy Bios Mode?
BIOS
UEFI
Runs on Legacy Hardware
Runs on both legacy and newer hardware
Only supports DOS and Windows
Supports Windows, Linux, and Mac operating systems
Smaller file size and uses less memory
Larger file size and uses more memory but provides more functionality
Boots via traditional method from MBR
Boots via modern method from GPT partition
Limited to 2TB storage support
Supports storage devices larger than 2TB
Fixed 16-bit architecture
Modern 64-bit architecture that is upgradeable
Can only address lower memory
Supports High-resolution graphics and inputs
Firmware cannot be updated without a flash ROM chip
Firmware updates are easy and don’t require flash ROM chip replacement
Limitations in booting from external devices
Better support for booting from external devices like USB, SD cards, etc
How Do I Change Thunderbolt Settings In BIOS?
Restart your computer and press the appropriate key (like F2, Del, Esc, or F10) to enter the BIOS setup utility.
Use arrow keys to find the "Advanced" or "Peripheral Configuration" section.
Look for options like "Thunderbolt Configuration" or "Thunderbolt Security."
Modify settings such as security levels, port configurations, and device enumeration based on your needs.
Select "Save Changes and Exit" to apply your settings and reboot the system.How To Unlock Advanced Settings In BIOS?
What is the difference between BIOS and UEFI?
What is the difference between UEFI and Legacy BIOS?
Is It Safe To Change Bios Mode?
Am I on UEFI or BIOS?
Why BIOS is better than UEFI?
Why is UEFI called BIOS?
Which is faster legacy or UEFI?
How to check BIOS?
Share This Article:
Water Treatment Skid,Commercial Ultrafiltration Skid,Commercial Ro Water Purifier,Skid-Mounted Water Treatment Systems Foshan Hongjun Water Treatment Equipment Co. Ltd , https://www.hjwastewatertreatment.com